Property Types
Real estate investments come in many forms. Understanding the different property types is essential for making informed investment decisions. Each property type has its own characteristics, risk profile, and potential returns.
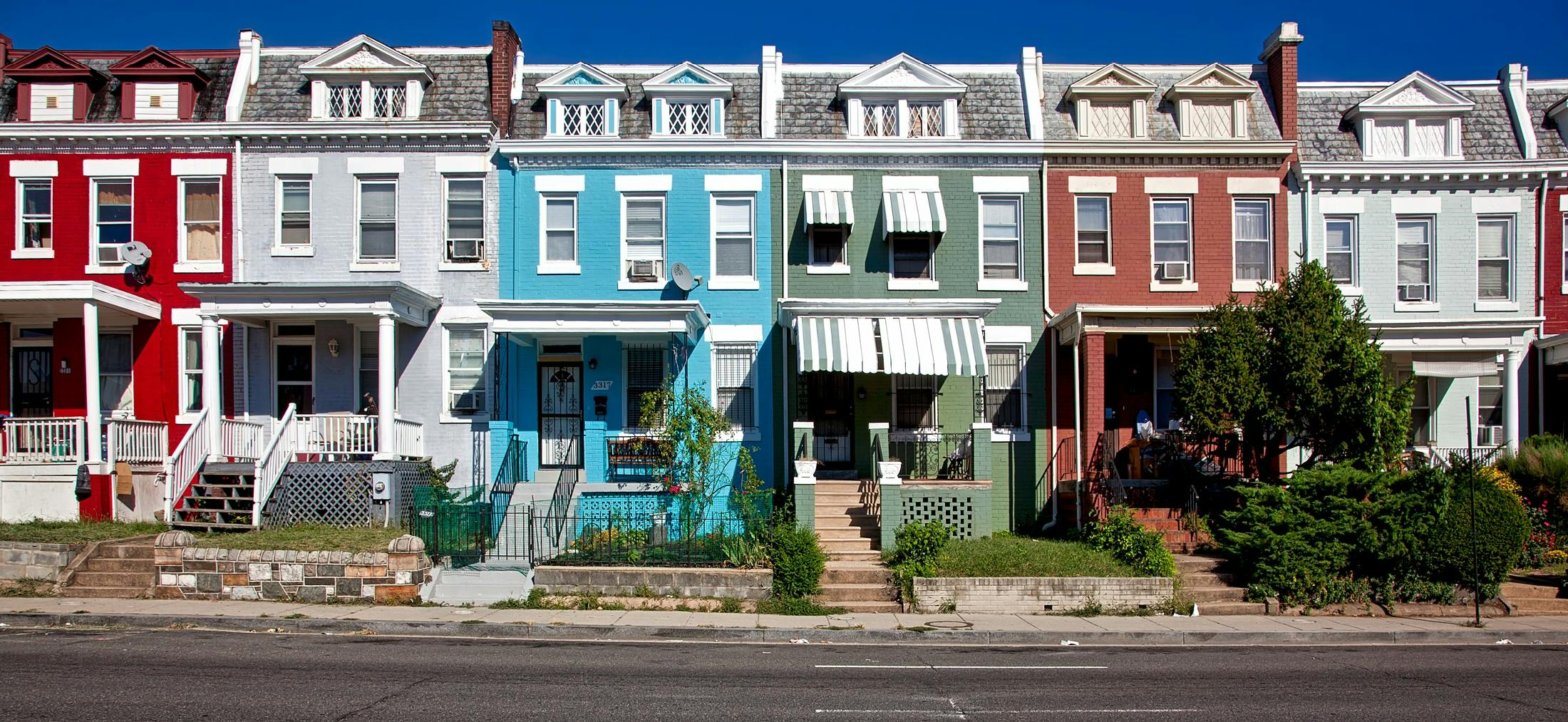

Properties designed for people to live in, including single-family homes, multi-family apartments, condos, and townhouses.
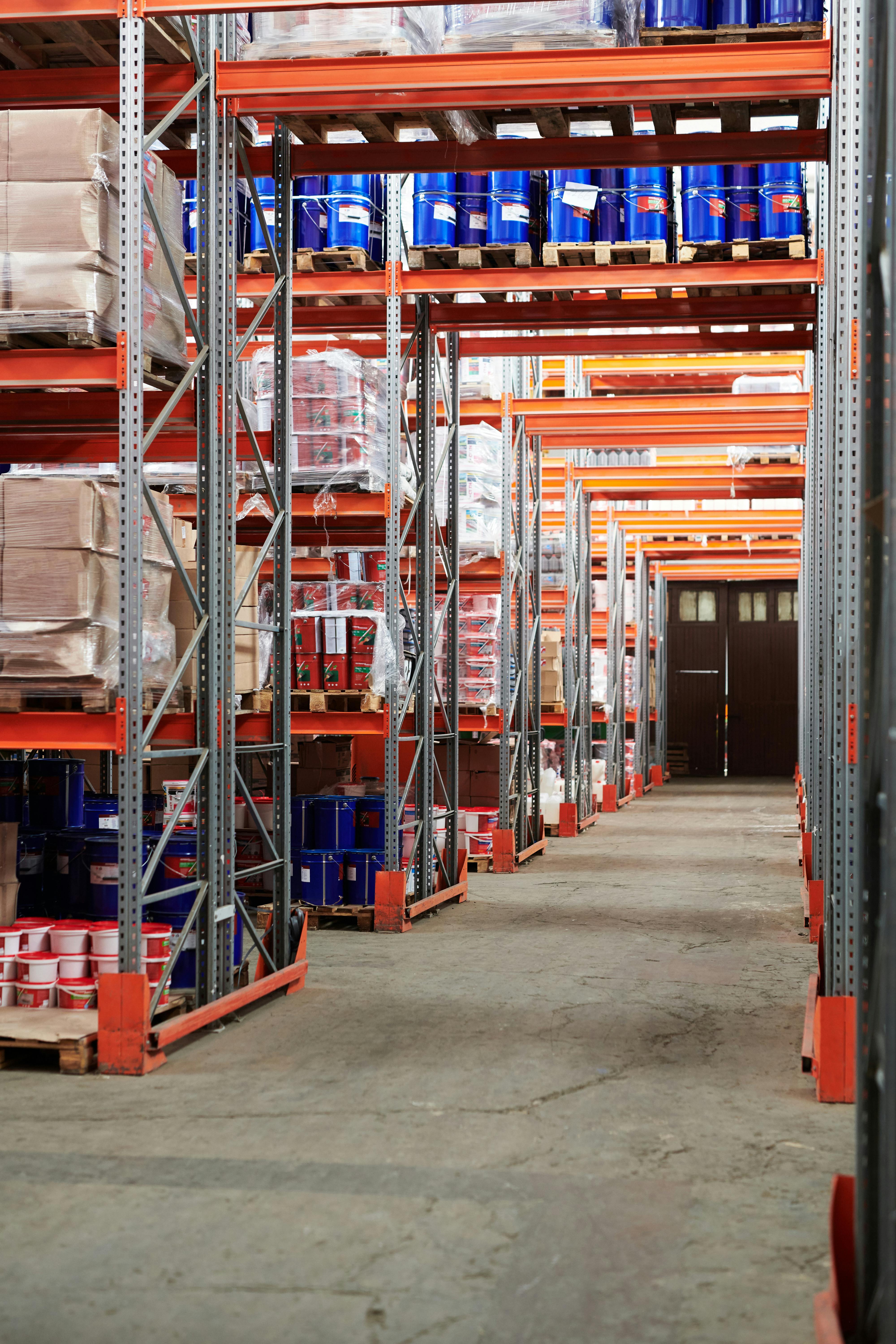

Properties used for business purposes, including office buildings, retail spaces, industrial warehouses, and hotels.
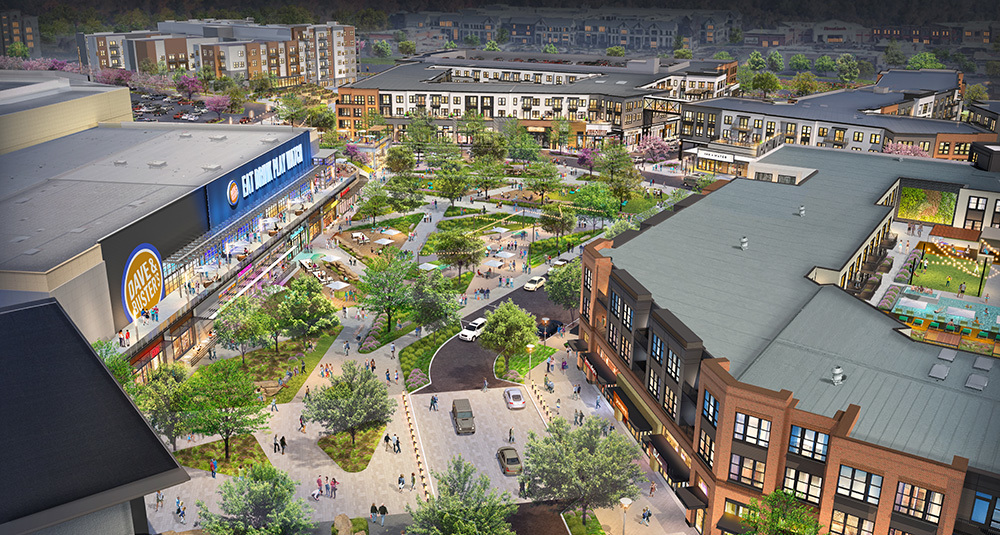

Properties that combine multiple uses, such as retail on the ground floor with residential units above.

Undeveloped property that can be held for future development or appreciation, including agricultural land.
Development Status
Properties can be categorized based on their development stage, which significantly impacts the risk and potential return profile of the investment.

These are projects where a property is being built from the ground up or undergoing major renovations.
- ✓Higher potential returns
- ✓Value creation opportunity
- ✗Higher risk (construction, timing, budget)
- ✗No immediate cash flow

These are completed properties that are already leased and generating steady income.
- ✓Immediate cash flow
- ✓Lower risk profile
- ✓More predictable returns
- ✗Typically lower overall returns
Common Deal Structures
Real estate investments are typically structured as either equity or debt investments, each offering different risk-return profiles and investor rights.
Equity Investments
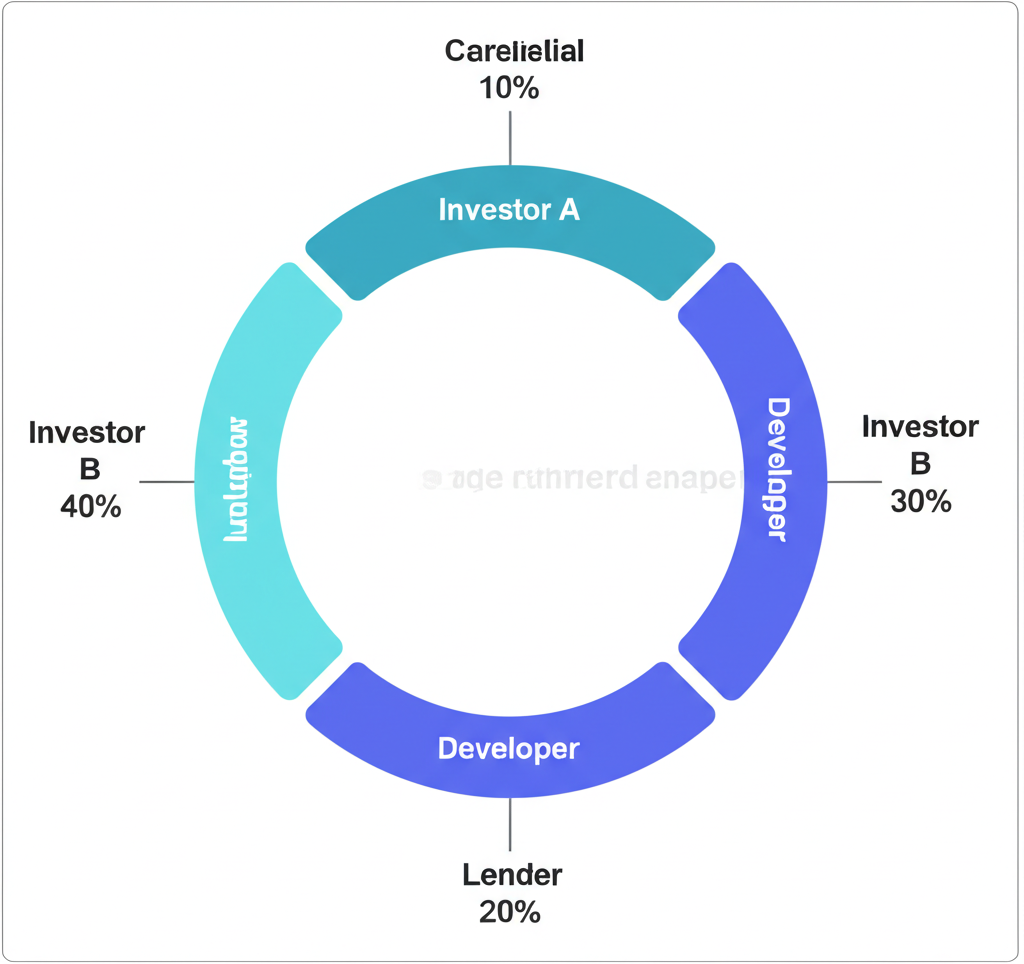
In equity investments, you own a share of the property itself. Your returns come from:
- 1Cash Distributions: Your share of the rental income after expenses.
- 2Appreciation: Increase in property value over time.
- 3Tax Benefits: Potential depreciation and other tax advantages.
Example: Investing $10,000 for a 1% ownership stake in an apartment complex, receiving quarterly distributions and a share of profits when the property sells.
Debt Investments
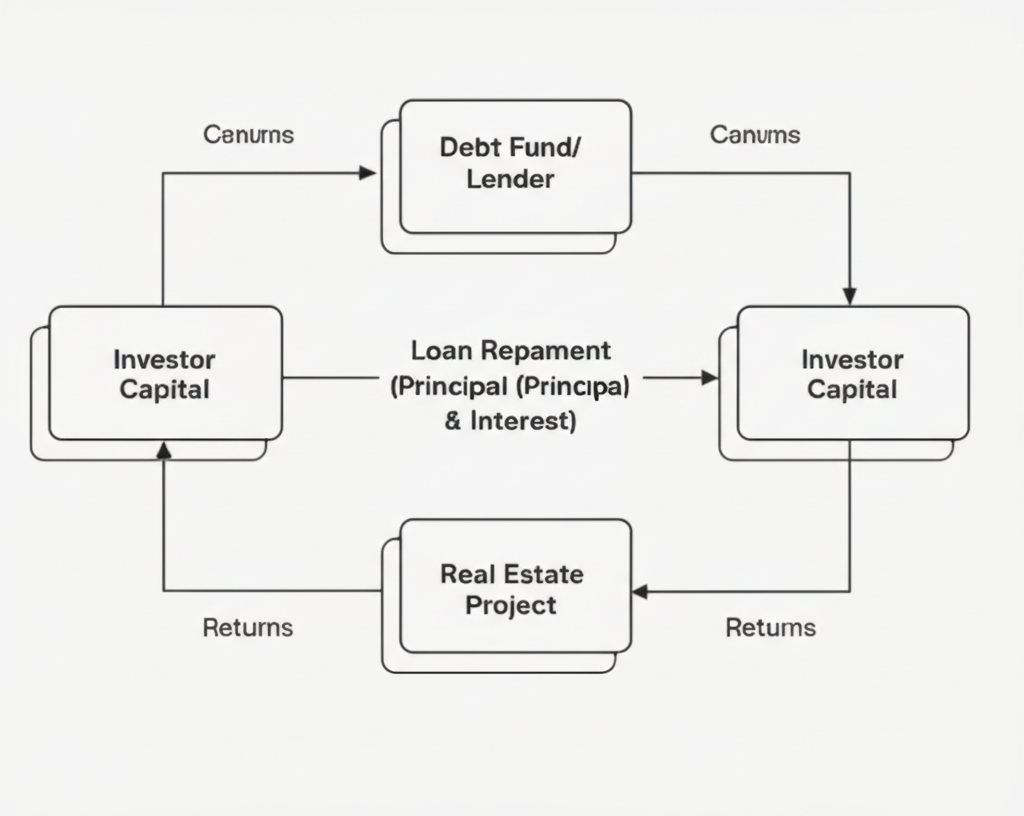
In debt investments, you're essentially lending money to a real estate project. Your returns come from:
- 1Interest Payments: Regular fixed payments based on your loan amount.
- 2Principal Repayment: Return of your original investment at the end of the term.
Example: Investing $10,000 in a real estate loan that pays 8% annual interest for a 12-month term, with your principal returned at the end.
Key Takeaway
"Different properties, different goals. Understanding the asset helps you choose the right opportunity."